Over 430M+ tonnes of new plastic is produced annually and projections indicate this could nearly triple by 2060 if this trend goes unchecked2. The current plastic production and consumption system is highly inefficient, relying on oil and gas extraction to create single-use plastics that are quickly discarded. Consequently, 79% of plastic waste goes in landfills or pollutes natural environments, 12% is incinerated, and under 10% is recycled, leading to severe environmental and ecological impacts from this unsustainable model3. Addressing this crisis through improved recycling solutions and other mitigation strategies is essential to protect biodiversity, mitigate climate change, and safeguard human health.
Tracxn identifies Plastic Waste Management Tech as a diverse range of startups addressing the plastic waste challenge through advanced technologies and sustainable solutions. The sectors and themes within this space are illustrated in the market map below:
As of 2025 YTD, 900+ startups operate globally in the Plastic Waste Management Tech space, of which over 450 have secured funding. Among these, 106 have secured Series A or later rounds, 40 have secured Series B or later rounds, and 24 have secured Series C or later rounds.
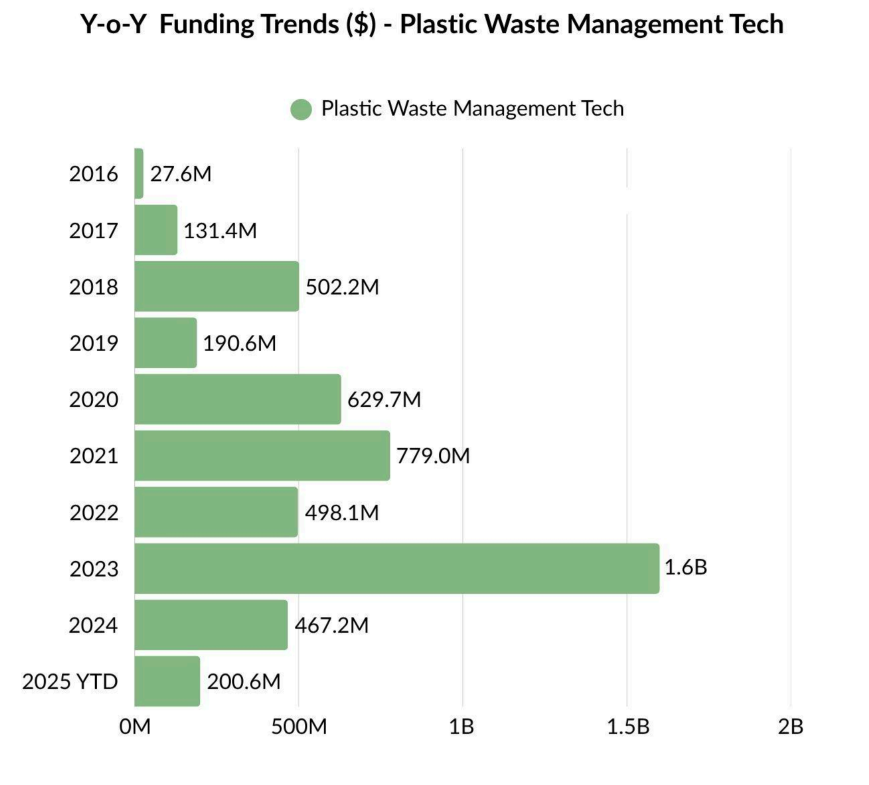
Funding activity in this space (Plastic Waste Management Tech) consistently exceeded $450M annually between 2020 and 2024, peaking at $1.6B in 2023 — largely driven by Footprint’s $830M Series E mega-round. In 2024, the total funding moderated to $467M, aligning more closely with pre-2023 levels.
The US has been the dominant recipient of funding in the Plastic Waste Management Tech space, attracting a cumulative $3B as of 2025 YTD. Europe has secured $1.2B in funding, driven primarily by the UK ($489M), Germany ($304M), and France ($123M). Other notable countries such as Singapore, Australia, and India have attracted $264M, $129M, and $100M in funding, respectively. Accordingly, this section compares the funding trajectories of the US, Europe, and India — regions that represent a mix of mature, scaling, and emerging ecosystems in this space. Since the beginning of this decade (2020 onwards), 2023 marked the peak year for funding across the US, Europe, and India, followed by a moderation in activity.
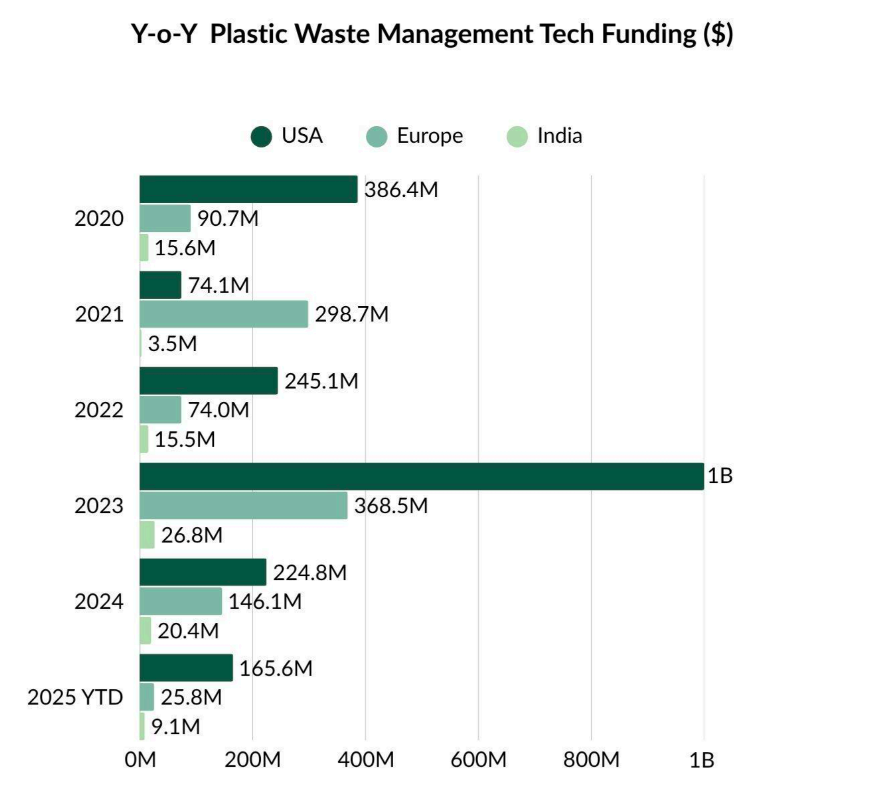
The US leads the Plastic Waste Management Tech funding, likely driven by generating ~40 million tons of plastic waste annually, surpassing all EU nations combined. Policy measures such as Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws—which make producers accountable for recycling and disposal—California’s SB 54 mandating recyclable packaging targets, and the EPA’s National Strategy to Prevent Plastic Pollution have created a strong regulatory push. Coupled with robust R&D infrastructure, these factors have created fertile ground for investment and technological advancement in plastic waste management solutions.
When comparing the funding trajectories of the US, Europe, and India in the Plastic Waste Management Tech space, a clear shift emerges over 2020 to 2024. While the US continues to lead in absolute funding, its global share declined from 61.4% in 2020 to 48.1% in 2024. In contrast, Europe’s share rose from 14.4% to 31.2%, and India’s from 2.5% to 4.5%, reflecting stronger policies and startup growth in these regions.
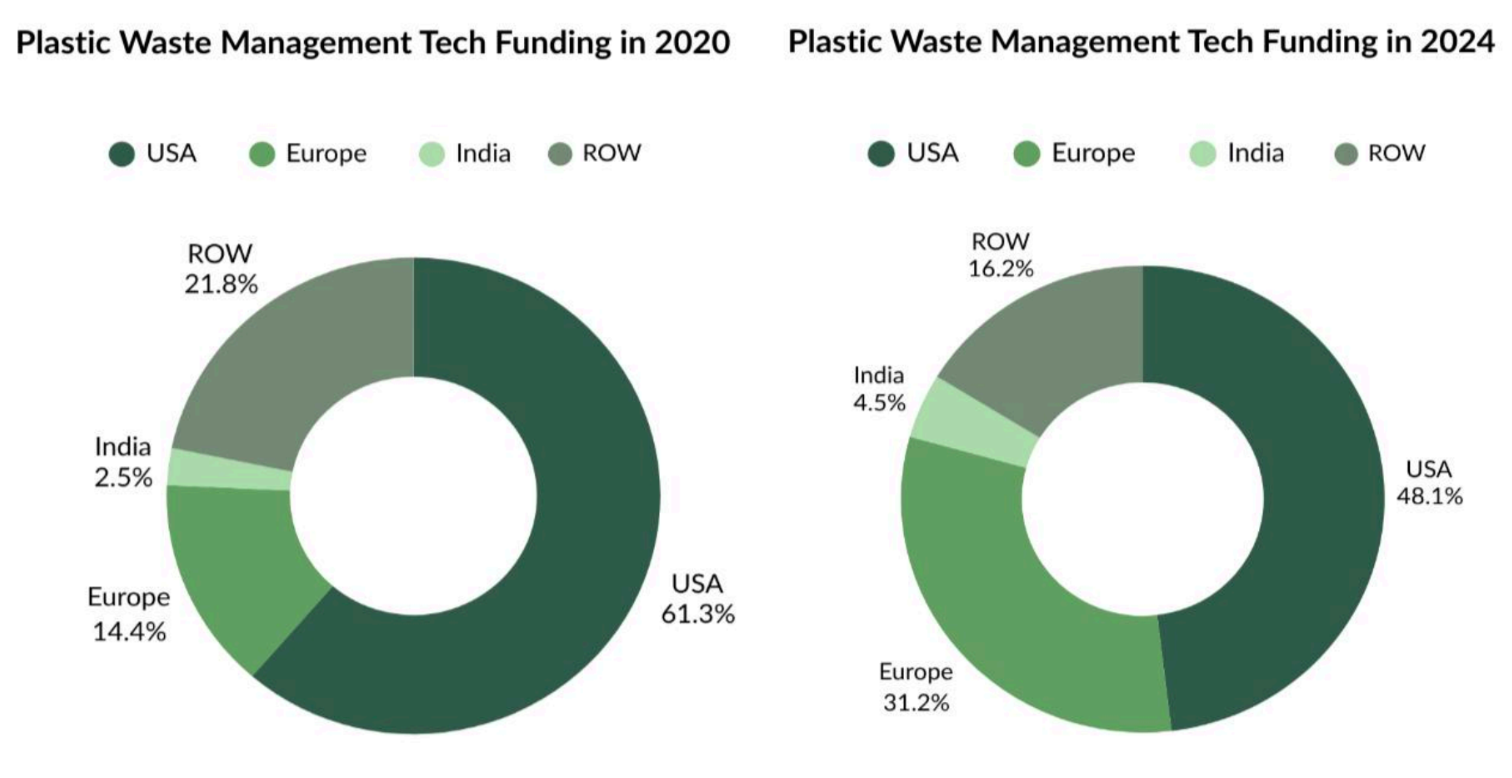
Europe’s share in Plastic Waste Management Tech funding rose from 14.4% in 2020 to 31.2% in 2024, likely driven by stringent EU regulations. Key Drivers include:
The likely key drivers contributing to India's increased share include:
These regulatory measures have likely catalyzed increased investment in sustainable waste management technologies across the above regions.
Since 2020, VCs have invested at least $200M annually in Plastic Waste Management Tech, with an average allocation of $433M from 2020–2024, up from $146M between 2016–2019, reflecting growing investor focus on sustainability.
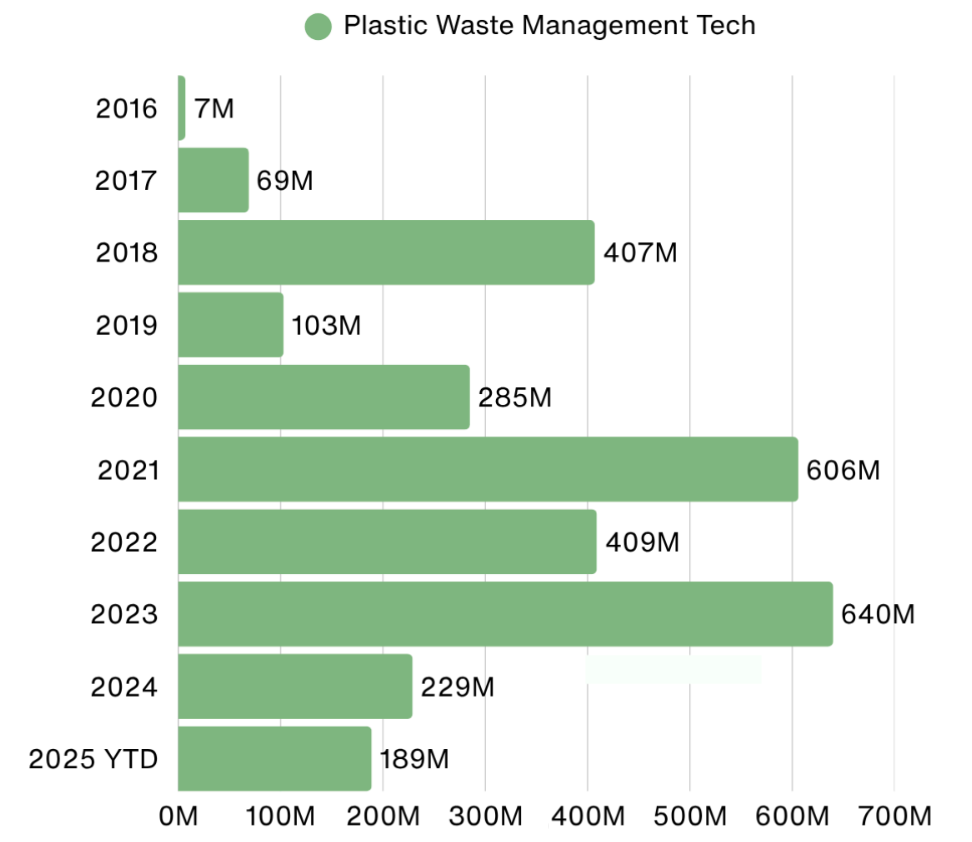
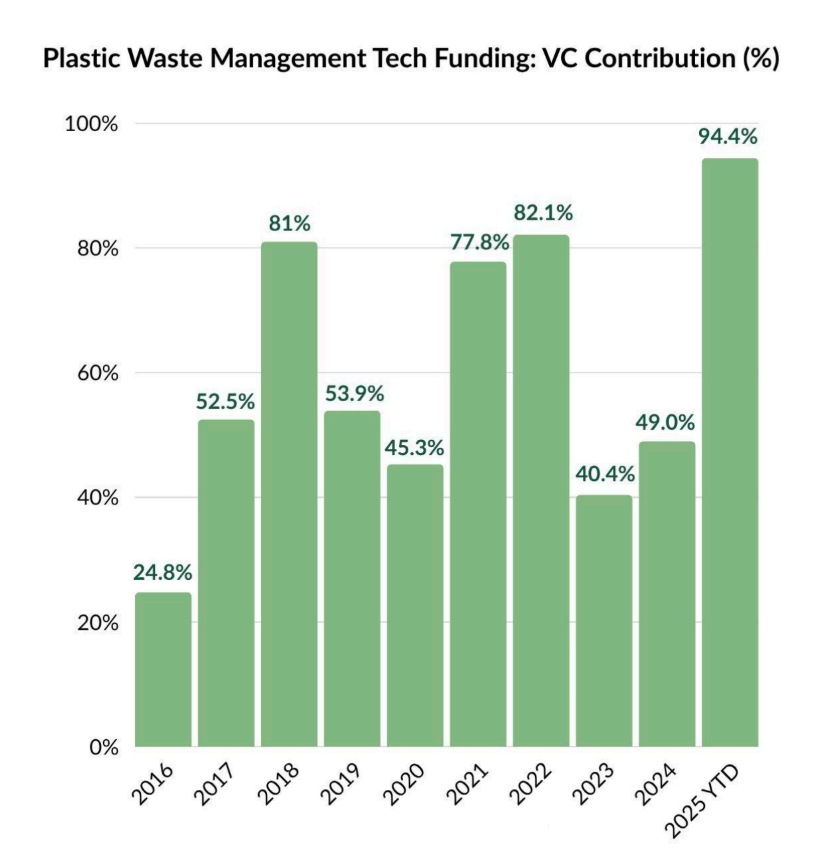
VCs have increasingly focused on Plastic Waste Management Tech, as reflected in their average contribution to Total Plastic Waste Management Funding, rising from 53% during 2016–2019 to 59% in 2020–2024. This is driven by favorable macroeconomics, supportive government initiatives alongside other reasons around circular economy.
Around 300 VCs have invested in Plastic Waste Management Tech till 2025 YTD. Among them, Circulate Capital has been the most active investor with 9 funding rounds. It is closely followed by Horizons Ventures and HTGF. The table below lists the top 10 most active VCs, with nearly half of them being environment and climate-focused.
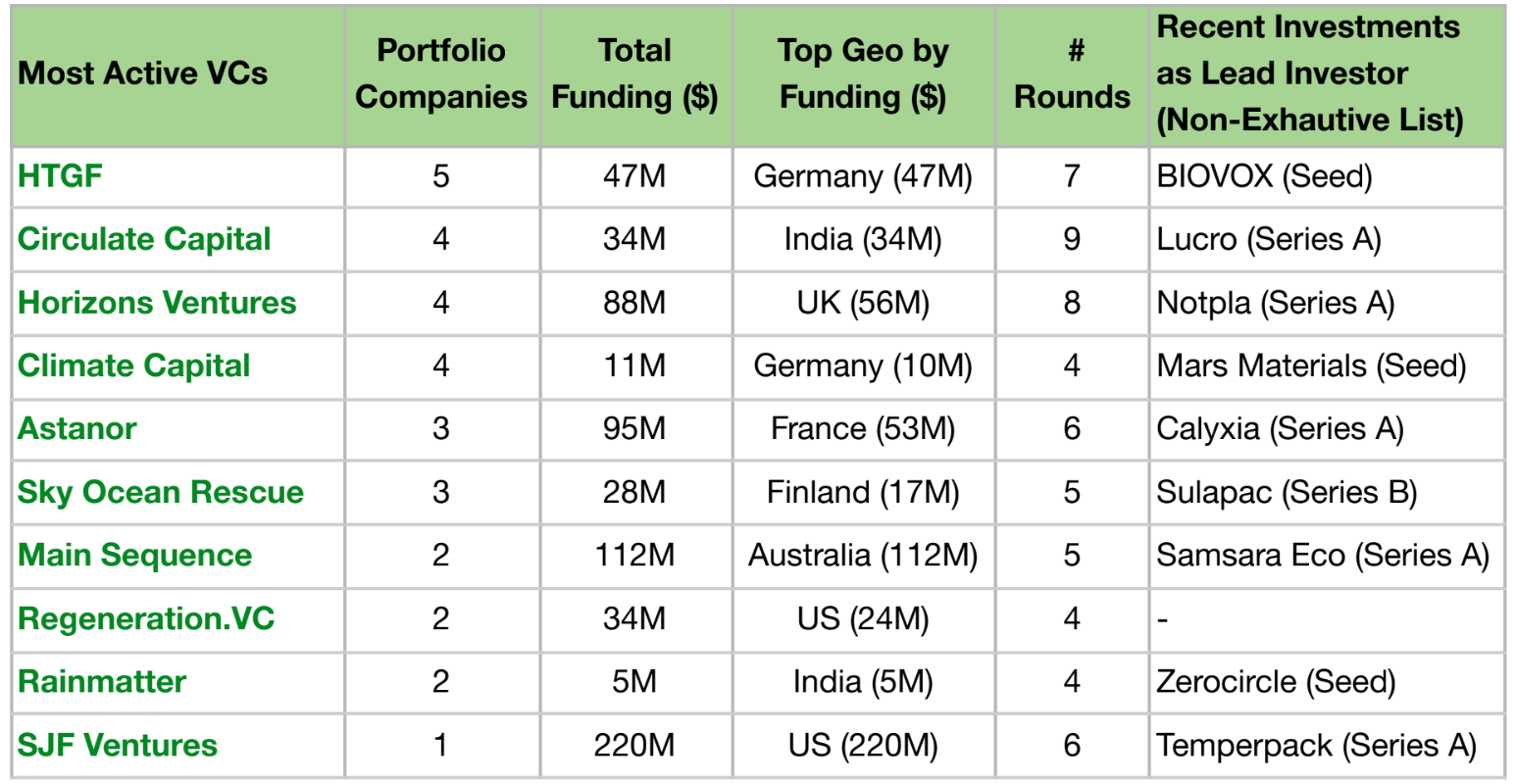
These VCs are investing in Plastic Waste Management Tech to tackle plastic pollution with innovative and scalable circular economy solutions. Circulate Capital’s investment in Lucro which will expand its plastic waste processing capacity to 315,000 tonnes, while Horizons Ventures’ funding in Notpla would boost the development of its seaweed fibre paper.
As of 2025 YTD, Plastic Waste Management Tech has witnessed 50 exits globally, comprising 36 acquisitions and 14 IPOs. Since 2020, the acquisitions peaked at nine in 2022, while the IPO activity reached its highest level with two listings each in 2021 and 2023.
Exit activity in 2024 was lower than in 2023, mirroring a broader decline in the global tech ecosystem, where acquisitions peaked at over 6300 in 2021 and IPOs exceeded 1100 in 2021, followed by steady declines through 2024 due to market challenges.
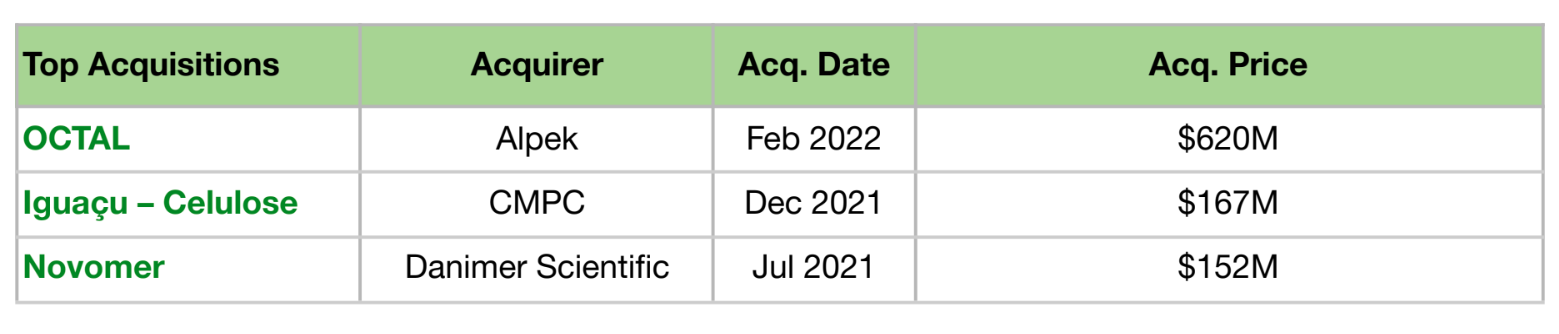
Acquisitions in this space reflect a broader push by established players to integrate innovative technologies, expand market presence, and enhance product portfolios to drive cost efficiency and sustainability. Notable examples include acquisitions of OCTAL, Iguaçu – Celulose and Novomer. Alpek’s $620M acquisition of OCTAL enabled vertical integration, added proprietary low-emission PET technology, expanded market reach, and was immediately EBITDA-accretive. CMPC’s $167M acquisition of Iguaçu Celulose expanded its presence in Brazil, diversified its paper product portfolio, and secured key forest-based raw materials. Danimer Scientific’s $152M acquisition of Novomer brought advanced, cost-efficient polymer technology, reduced production costs, and enhanced its biodegradable product lineup through strong product synergy.
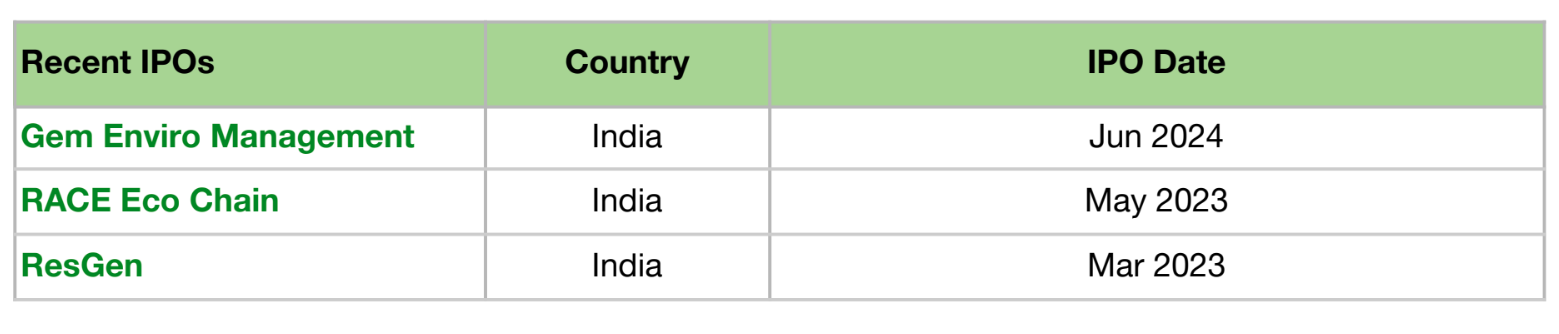
In the recent years (2023 and 2024), three startups from Plastic Waste Management Tech went public: Gem Enviro Management, RACE Eco Chain and ResGen. GEM Enviro Management raised funds to support working capital needs and general corporate purposes. ResGen Limited planned to use the IPO proceeds to boost working capital, purchase its manufacturing facility land, and meet general corporate needs. Race Eco Chain Ltd aimed to strengthen its long-term working capital through the IPO.
There are over 900 startups worldwide in the Plastic Waste Management Tech, with nearly 50% of them (450+) having received funding. The US leads with over 100 funded startups, a position supported by its mature funding ecosystem and dense concentration of innovative players. The UK, India, and others follow - marking their presence in the evolving global landscape.
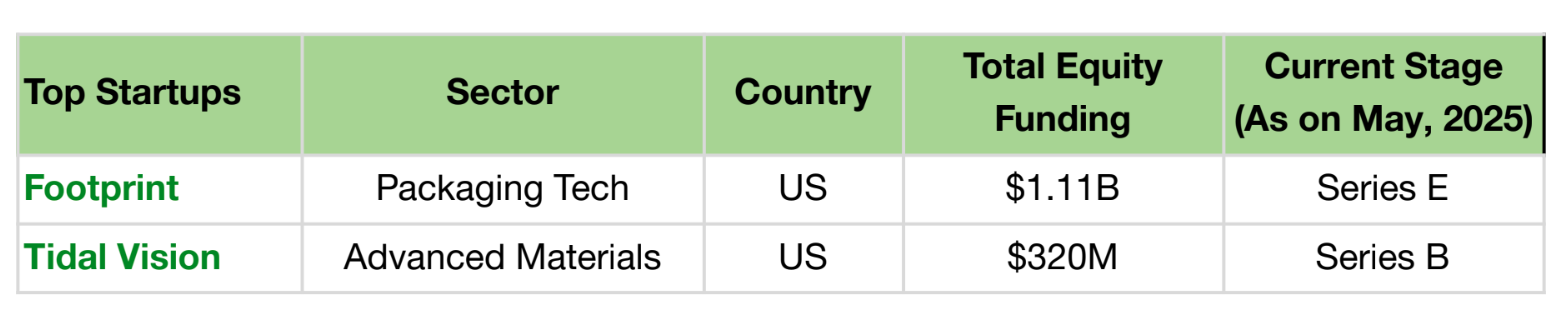
Among the most funded startups in this space, the top two—Footprint and Tidal Vision—are based in the US.
The funded startups are attracting investments as they align with sustainability trends, offering eco-friendly solutions backed by strong market demand and potential for long-term growth. Investors are focusing on companies that combine innovation with clear use cases and operational scale.
For example, Footprint has received the highest funding that could be attributed to its strong revenue growth and demand driven by regulations against single-use plastics. Its partnership with major companies like McDonald’s and Procter & Gamble enable eco-friendly packaging solutions, driving its growth. Further, innovative plant-based packaging that reduces reliance on traditional plastics, reflects its alignment with current sustainability needs.
Tidal Vision secured funding for its chitosan-based solutions that are used in water treatment, agriculture, and material science. These applications offer both environmental and business value.
Apart from the top funded startups, there are several other notable startups making an impact in Plastic Waste Management Tech. The table below highlights a few of them, each at different stages of their growth journey.
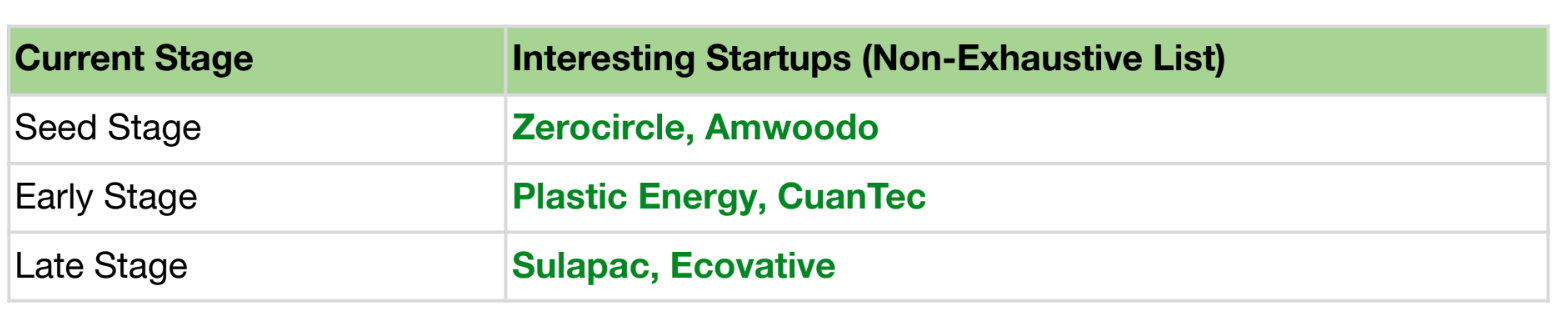
The increased interest in these startups stems from their focus on sustainable materials, addressing high-demand, low-supply markets driven by global demand for eco-friendly solutions. This is reflected in startups such as Zerocircle, Plastic Energy, Sulapac and Ecocative. Zerocircle focuses on seaweed-based packaging solutions. Plastic Energy converts end-of-life plastic into feedstock, which replaces fossil oils in the production of new plastics. Sulapac which develops biodegradable packaging for cosmetics and food, capitalizing on the scarcity of microplastic-free alternatives. Similarly, Ecovative leverages mycelium-based materials for packaging and construction, addressing the high demand for low-carbon alternatives in markets with insufficient sustainable supply. These companies thrive by filling critical gaps in markets prioritizing sustainability amid regulatory and consumer-driven shifts.
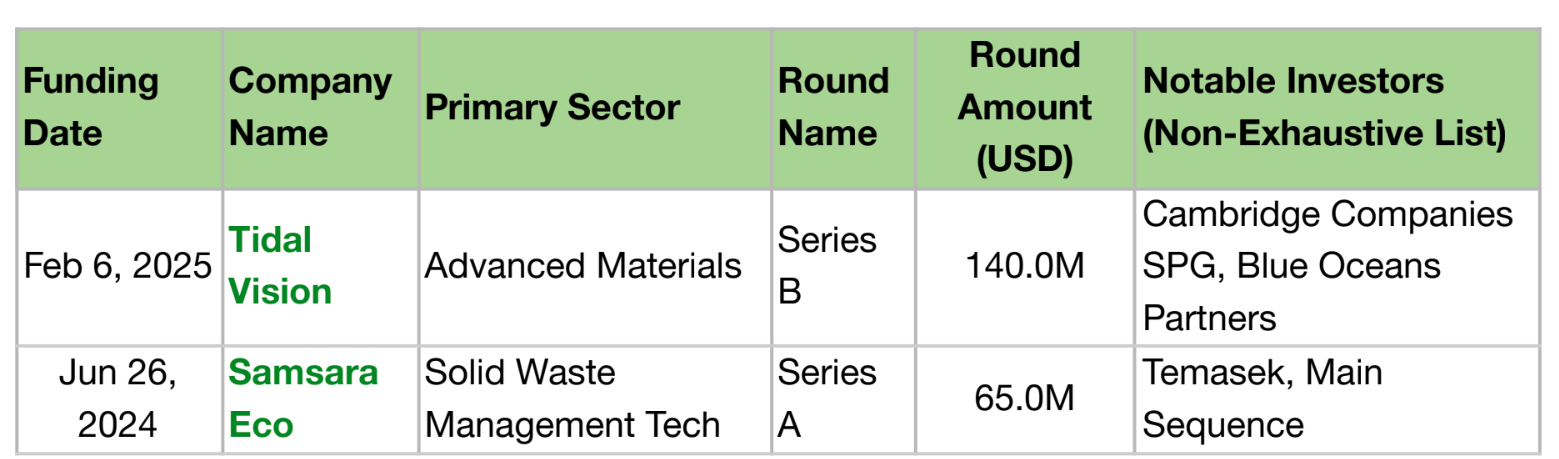
In the past year, the Plastic Waste Management Tech space witnessed two major funding rounds—Tidal Vision in the Advanced Materials sector and Samsara Eco in Solid Waste Management. Notable VCs, including Cambridge Companies SPG, Blue Oceans Partners, and IDO Investments, backed Tidal Vision’s $140M Series B round on February 6, 2025. Temasek, the sole PE investor, co-led Samsara Eco’s $65M Series A round on June 26, 2024, with VC Main Sequence. While Tidal Vision will use the funds for increasing production capacity of chitosan-based solutions and boosting R&D efforts, Samsara Eco, focused on enzymatic recycling of plastics, plans to allocate its funding to build commercial facilities in Southeast Asia.
The following brief identifies and outlines the sub-sectors within the Plastic Waste Management, providing definitions and context for each category referenced and considered in the report
The brief outline of various sub-sectors are stated below:
- Solid Waste Management Tech: Startups focussed on collection, recycling, upcycling of plastic, bioplastics and plastic offsetting.
- Advanced Materials: Startups innovating on Biomaterials (biodegradable polymers and sustainable fabrics) and Sustainable fabrics.
- 3D Printing: Startups focussed on recycled plastic filaments and natural fiber composites.
- Packaging Tech: Startups innovating in recyclable, reusable, and bio-based packaging solutions.
- Construction Tech: Startups Startups focussed on recycled plastics as eco-friendly building materials and in modular construction
- Chemicals Tech: Startups working on green additives made from plastic waste. - Sustainable Consumer Products: Integrating recycled plastics in consumer products (apparels, accessories etc).
- Air Pollution Management Tech: Startups innovating on Biodegradable/Bioplastics/Plastic-related products from captured carbon.
The last decade (2015-2025) has seen numerous events across the world that were oriented towards recognition and mitigation of plastic-waste. Below are some of the key events in chronological order that elaborates on the same.
The Global Awakening to Plastic Waste (2015-2017): In 2015, all UN member states adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which included ‘SDG 12’ on Responsible Consumption and Production—signaling a global commitment to sustainable waste management, including plastics. In 2016, the Ellen MacArthur Foundation launched the New Plastics Economy, promoting a circular economy approach to rethinking plastic design and use. In 2017, the United Nations Environment Programme(UNEP) launched today an unprecedented global campaign to eliminate major sources of marine litter: microplastics in cosmetics and the excessive, wasteful usage of single-use plastic by the year 2022.
China’s Import Ban & The Basel Convention Amendment (2018-2019): In 2018, China’s ban on plastic waste imports disrupted global waste trade dynamics, exposing the reliance of wealthy nations on exporting waste to developing countries and prompting calls for better domestic waste management systems. In 2019, the Basel Convention, a key international agreement regulating hazardous waste, was amended to include plastic waste, marking the first global treaty to directly address plastic pollution.
A Surge in Global Commitment (2020-2023): The Covid-19 pandemic increased the levels of both macro (e.g. large particles) and micro plastic (e.g. plastic fragments less than 5 mm in length) waste. This could have further triggered the due attention that plastic waste needed. In 2022, the UN Environment Assembly adopted a historic resolution to forge an international legally binding agreement by 2024 to end plastic pollution. In the same year, The World Bank released frameworks and funding tools to support circular plastic waste management in urban areas across developing countries, emphasizing upstream solutions like eco-design and recycling innovation. In 2023, UNEP released a report outlining how plastic pollution could be reduced by 80% by 2040 using existing technologies and systemic shifts. Further, in Nov-Dec 2023, For the first time, plastics were formally discussed in the climate negotiations at COP28, connecting plastic production to fossil fuel dependency and lifecycle emissions.
Intensifying Efforts & The Bigger Push (2024-2025): In 2024, The fifth session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-5) in Busan, South Korea, aimed to finalize the global plastics treaty but concluded without consensus. This discussion will be further continued in 2025.
These events underscore a critical shift toward circular economies and systemic solutions to address the escalating plastic pollution crisis.
N8
